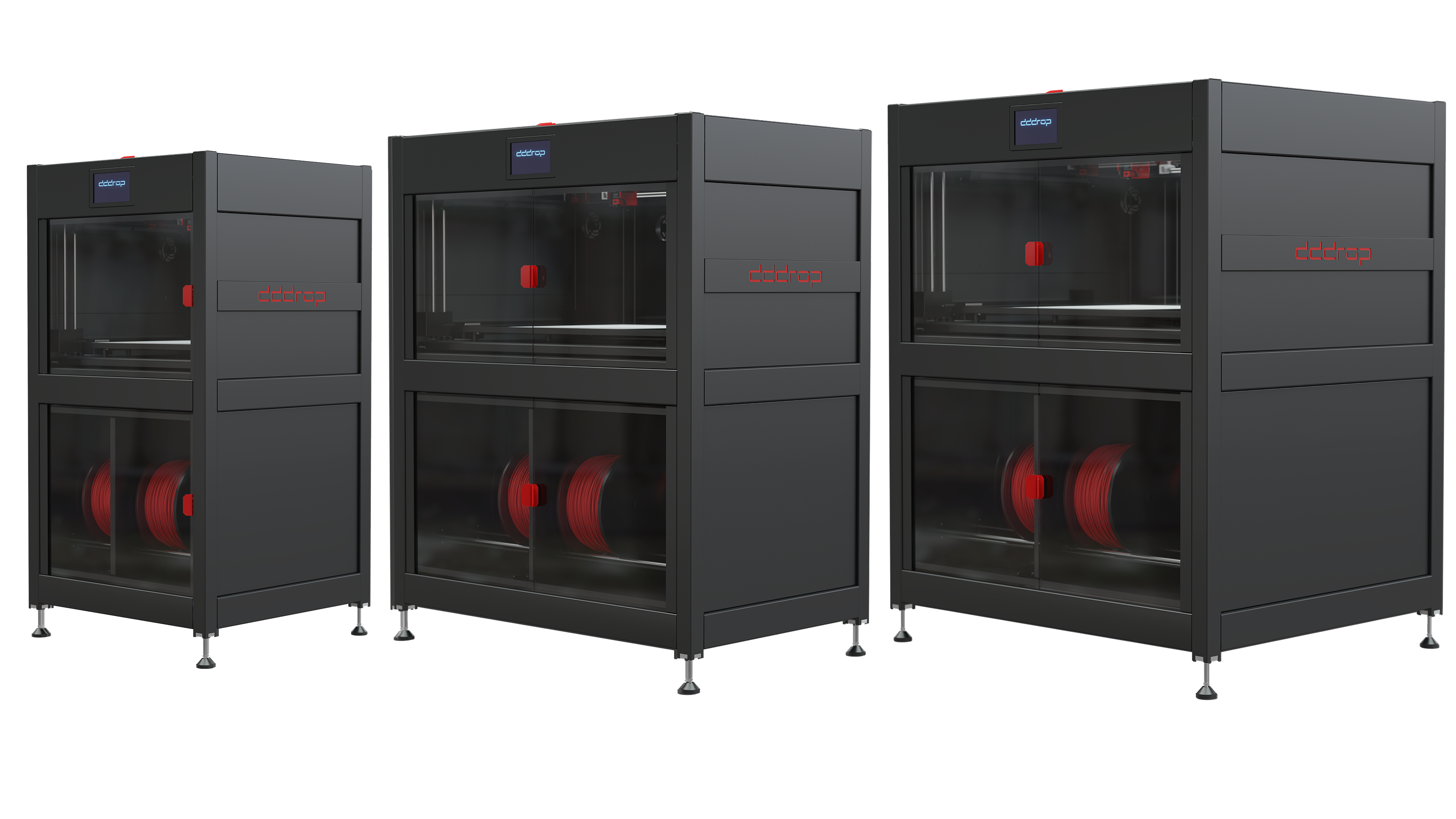
Optimising serial production with 3D printers
In an era when speed and efficiency are the backbone of industrial activities, series production is central to the quest for competitive advantage. The landscape of manufacturing processes is constantly evolving, and one of the most notable innovations driving this revolution is the rise of 3D printing.
Change in the way of serial production.
Traditional methods of serial production were characterised by complex and time-consuming processes, with significant overheads and limitations on design freedom. But 3D printing has broken these conventional boundaries by adding a new dimension of flexibility and speed.
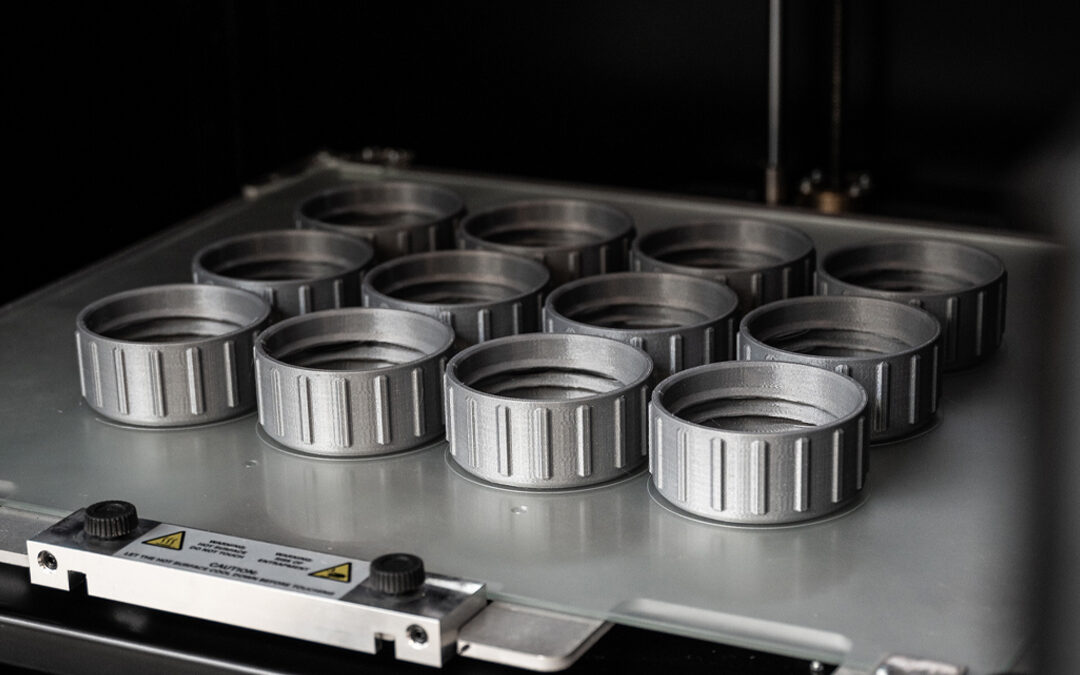
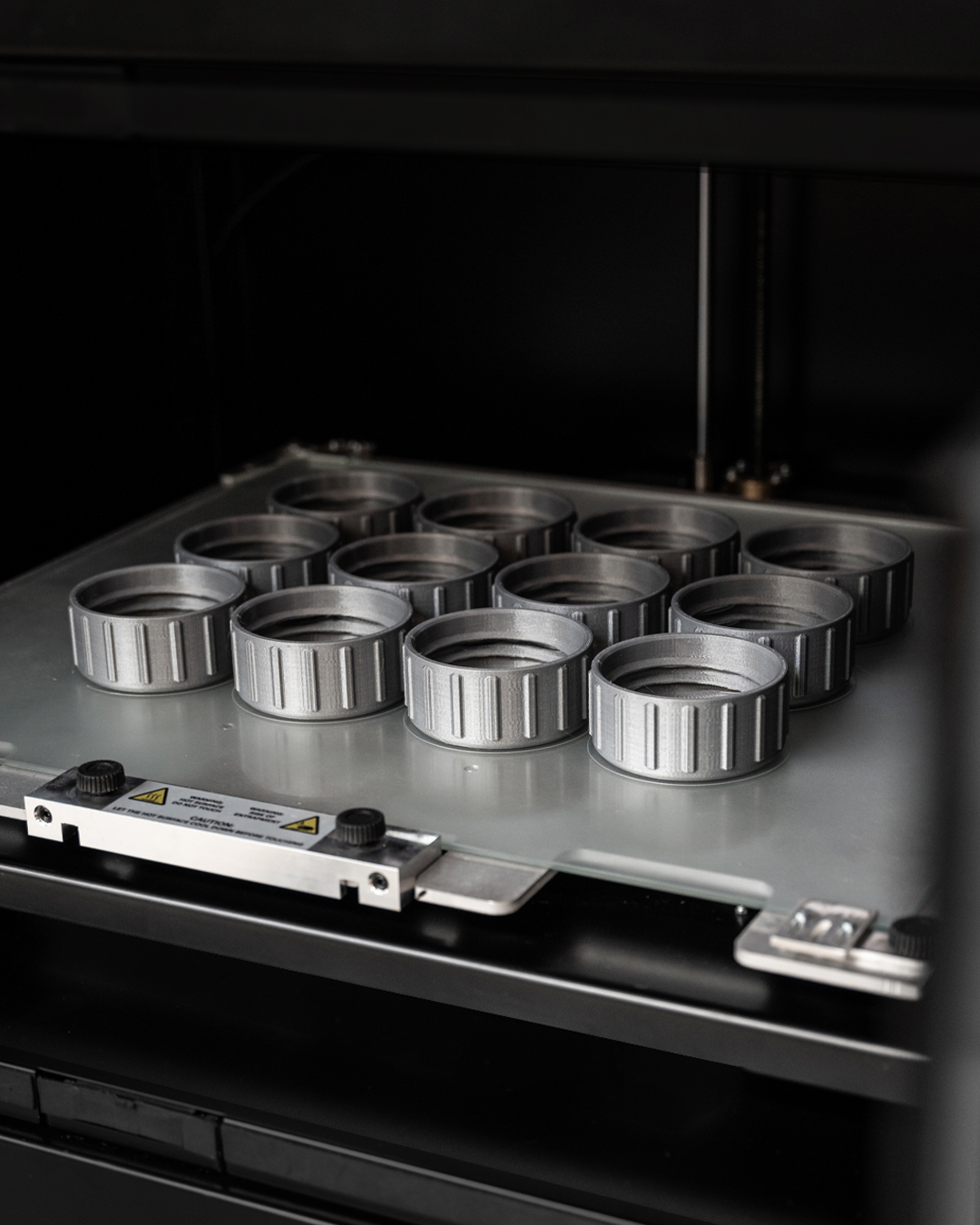
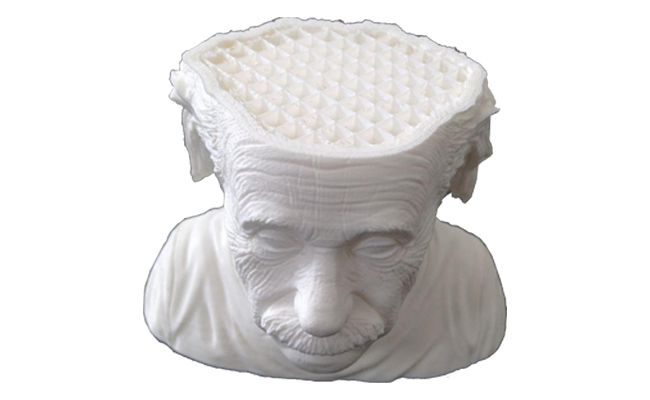
With 3D printing, manufacturers can realise complex geometries with unprecedented precision and reproducibility. This opens the door to new design possibilities previously unthinkable, allowing products to be optimised for performance and functionality.
Efficiency as a key point
Efficiency is the backbone of serial production, and 3D printing offers a range of benefits that enhance this efficiency. By eliminating tooling costs and minimising raw material wastage, 3D printing significantly reduces operational costs. Moreover, it enables on-demand production, which can optimise inventory levels and avoid excess inventory.
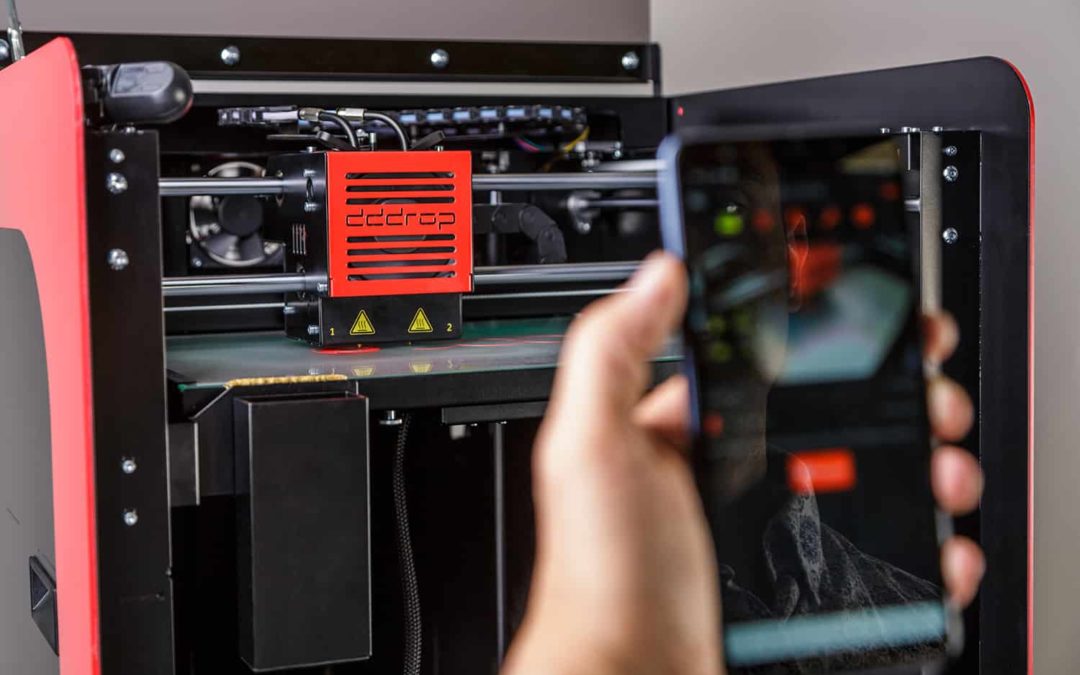
In addition, 3D printing enables manufacturers to take advantage of digital design and manufacturing processes. Through the use of advanced simulation software, designs can be validated before printing, identifying errors at an early stage and avoiding costly revisions. This reduces development time and accelerates time-to-market, giving companies a competitive advantage.
Quality and consistency
While speed and efficiency are vital, this should not come at the expense of quality and consistency. 3D printing, however, offers a high level of reproducibility, with each printed part being identical to the original. This reduces variability in the production process and ensures consistent quality of final products.
Moreover, the digital nature of 3D printing enables real-time monitoring and control, allowing any deviations to be detected and corrected in a timely manner. This increases the reliability of the production process and ensures consistent results across the entire series production.
Sustainability and environmental friendliness
In addition to operational benefits, 3D printing also contributes to sustainability and environmental friendliness. By minimising waste of raw materials and using recycled materials, 3D printing reduces the ecological footprint of series production. Moreover, local production centres can be set up, reducing transport costs and emissions.
Conclusion
In an era when speed, efficiency and quality are crucial to the success of mass production, 3D printing represents a revolutionary force. By breaking the traditional boundaries of manufacturing processes, 3D printing opens up new opportunities for manufacturers to innovate and excel in a competitive market.
With its ability to realise complex geometries, reduce costs and promote sustainability, 3D printing promises to have a lasting impact on the industry. As manufacturers strive to optimise series production, 3D printing will undoubtedly be an integral part of their strategies for success in the 21st century.