Pros and Cons of TPU for 3D Printing
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) has emerged as a go-to material for individuals and industries looking to 3D print flexible objects. Its properties provide a close resemblance to rubber while also being adaptable to the 3D printing process. However, like any material, TPU has its share of advantages and disadvantages when it comes to 3D printing. This section aims to delineate the pros and cons of utilizing TPU for 3D printing applications.
- Pros:
- Flexibility: TPU is highly flexible and can mimic the elasticity of rubber, making it ideal for a plethora of applications where flexibility is a requisite.
- Customizability: The hardness, heat resistance, and abrasion properties of TPU can be tailored to meet specific requirements, offering a level of customization that is hard to achieve with traditional rubber.
- Durable: TPU is known for its durability and resistance to abrasion, wear, and tear, which is crucial for industrial applications.
- Recyclability: Being a thermoplastic material, TPU can be recycled, which is beneficial from an environmental standpoint.
- Wide Range of Applications: From consumer goods like shoe soles and phone cases to industrial applications like sealing rings and hoses, TPU’s versatility is commendable.
- Cons:
- Printing Difficulty: Printing with TPU can be challenging, especially for beginners. It requires a well-calibrated printer and a good understanding of the printing settings.
- Printing Speed: TPU requires a slower printing speed compared to more rigid materials like PLA or ABS to ensure accurate deposition and to prevent issues like stringing.
- Printer Compatibility: Not all 3D printers are equipped to handle the flexibility of TPU. Printers with a direct drive extruder are generally better suited for printing with TPU.
- Cost: While TPU might be more cost-effective compared to some materials, it can still be on the higher side price-wise, especially when compared to more common 3D printing materials like PLA.
Understanding the benefits and challenges associated with TPU for 3D printing can aid individuals and enterprises in making informed decisions regarding whether it’s the right material for their specific projects. With the right equipment and expertise, the hurdles associated with TPU can be navigated, unlocking its full potential in 3D printing applications.
Application Examples of 3D Printed TPU
The versatility of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) transcends into a myriad of applications, where its rubber-like flexibility coupled with the precision of 3D printing brings forth innovative solutions. Below are some notable application examples of 3D printed TPU, demonstrating its potential in both consumer and industrial realms.
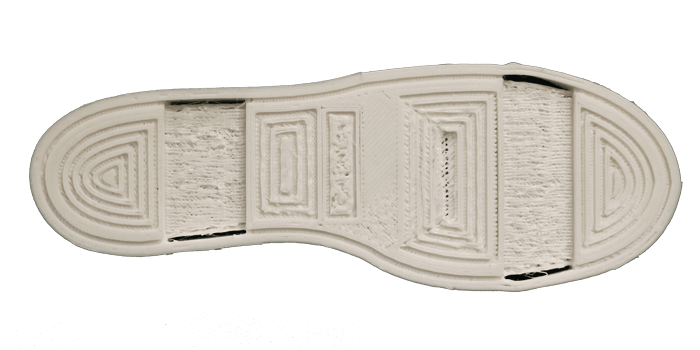
- Footwear:
- TPU is extensively used in the footwear industry to create flexible yet sturdy shoe soles. 3D printing with TPU allows for customized designs catering to different footwear needs, be it athletic shoes, orthopedic insoles, or fashion-forward footwear.
- Sealing Rings:
- The material’s inherent flexibility and durability make it a prime choice for manufacturing sealing rings. 3D printed TPU sealing rings can be tailored to fit specific dimensions and tolerances, ensuring a snug fit and effective sealing.
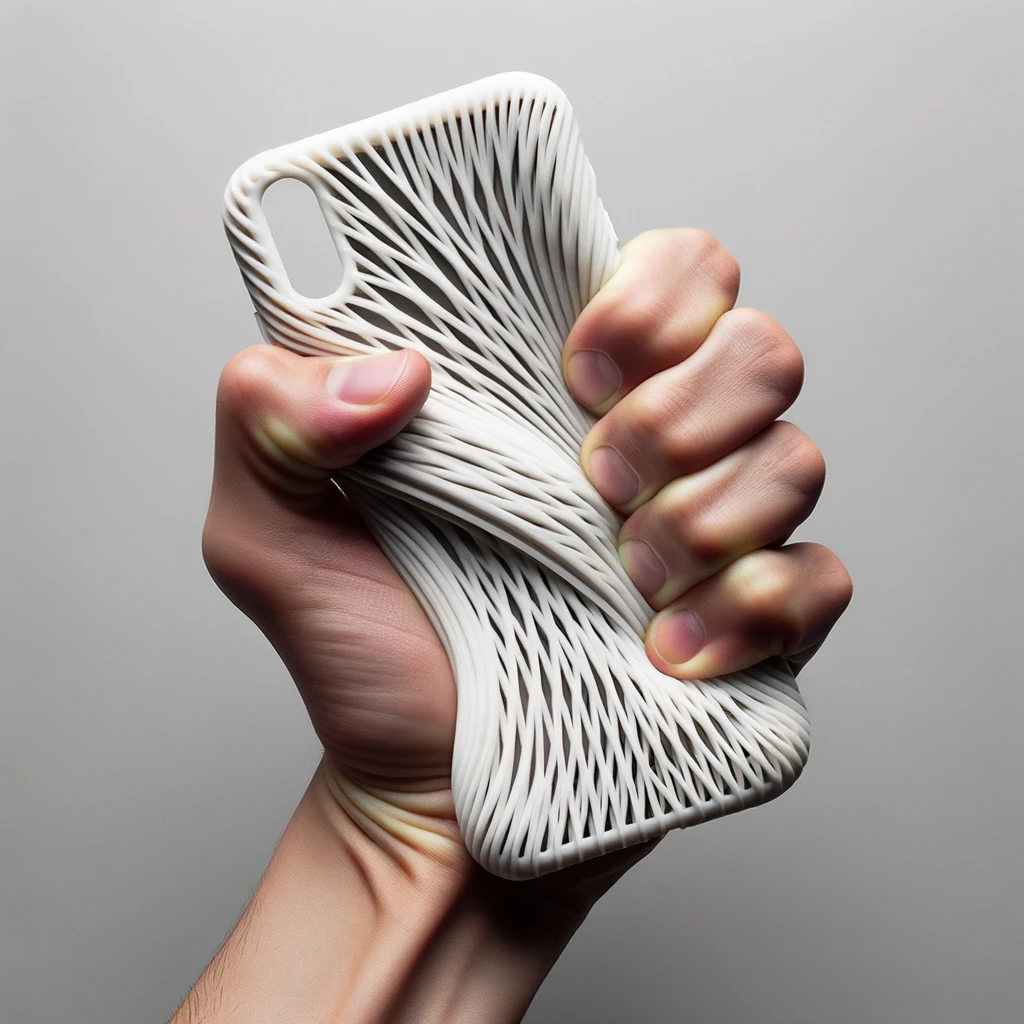
- Protective Cases:
- From smartphone cases to protective covers for electronics, 3D printed TPU offers a blend of shock absorption and aesthetic appeal. Its capacity to withstand daily wear and tear while maintaining a sleek appearance is highly valued.
- Medical Devices:
- In the medical field, TPU is utilized for creating flexible components like tubing, cushioning, and various wearable devices. Its biocompatible variants can be employed in direct contact with the body, making it a viable material for medical applications.
- Automotive Components:
- TPU’s resistance to abrasion and flexibility finds applications in the automotive industry for parts like bushings, couplings, and flexible hoses. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and customization of these components to suit specific vehicle models.
- Gaskets and Connectors:
- The capability of TPU to form airtight seals and withstand mechanical stress makes it a preferred material for gaskets and connectors. 3D printing these parts with TPU can ensure precise dimensions and enhanced performance.
- Sporting Goods:
- Items like custom grips, flexible guards, and performance-enhancing athletic gear can be 3D printed with TPU to cater to the individual needs of athletes, enhancing comfort and functionality.
- Customized Promotional Products:
- The ease of customization with 3D printing allows for the creation of personalized promotional products. TPU can be used to craft unique, branded items that are both functional and visually appealing.
These applications underscore the utility of TPU in the realm of 3D printing, fostering innovation across a broad spectrum of industries. The ability to tailor the material properties and geometries through 3D printing amplifies the advantages of TPU, making it a prized material for tackling complex design challenges.
What should I take into account when printing with TPU?
Printing with TPU is difficult. Therefore it is necessary to practice first with PLA before printing with TPU. TPU needs more time to melt and flow. If you print too fast, the material will collapse. Therefore it’s important to reduce the printing speed. Also, the kind of printer you use is relevant for printing TPU. In case the drive motor is located on the back of the printer, the material is pushed through the entire extruder to eventually melt in the print head. When using printers with a direct drive, where the motor is located in the print head, the filament doesn’t need to be pushed through the entire extruder. It only has to bridge a small distance, until it is melted. Imagine you push an elastic through a tube, the elastic will accumulate: the greater the distance, the more difficult it becomes. If the drive motor is located in the print head, the filament has to bridge a smaller distance. Thus, you need a printer with a direct drive to print well with TPU filament.
How to influence the flexibility?
Several TPE’s are available: ones that are really rigid and others really elastic. However, the elasticity of the final product is not only affected by the used filament. The printing technique also has influence on the elasticity. The thinner you print, the more elastic your product becomes. For example: printing a honeycomb structure creates thin layers with air between them. In this way you can determine which part is more flexible than the other. Thanks to the printing technique you can reach different levels of flexibility. When rubber is vulicanized, the end product is always solid. Thus it isn’t possible to play with the elasticity of rubber.