How to choose the right 3D printing material?
If you decide to 3D print a design, one of the first questions you need to ask yourself is; which filament am I going to use? There is a wide range of filaments available and as a beginner, it can be overwhelming. This blog will help you choose the right filament for your application, so you can be sure you’re getting started with the right filaments.
Who will use the 3D printer?
How warm is the environment in which the design is used?
For applications where your object will encounter heat, such as near a heat source or in direct sunlight, ABS is a good choice. It has a high glass temperature of 110°C, which makes it resistant to boiling water and other heat sources. PETG is slightly lower with a glass point of 90°C and is less able to withstand extreme temperatures. PLA and FLEX are the least heat-resistant, with a glass temperature around 60°C.
What are you going to print?
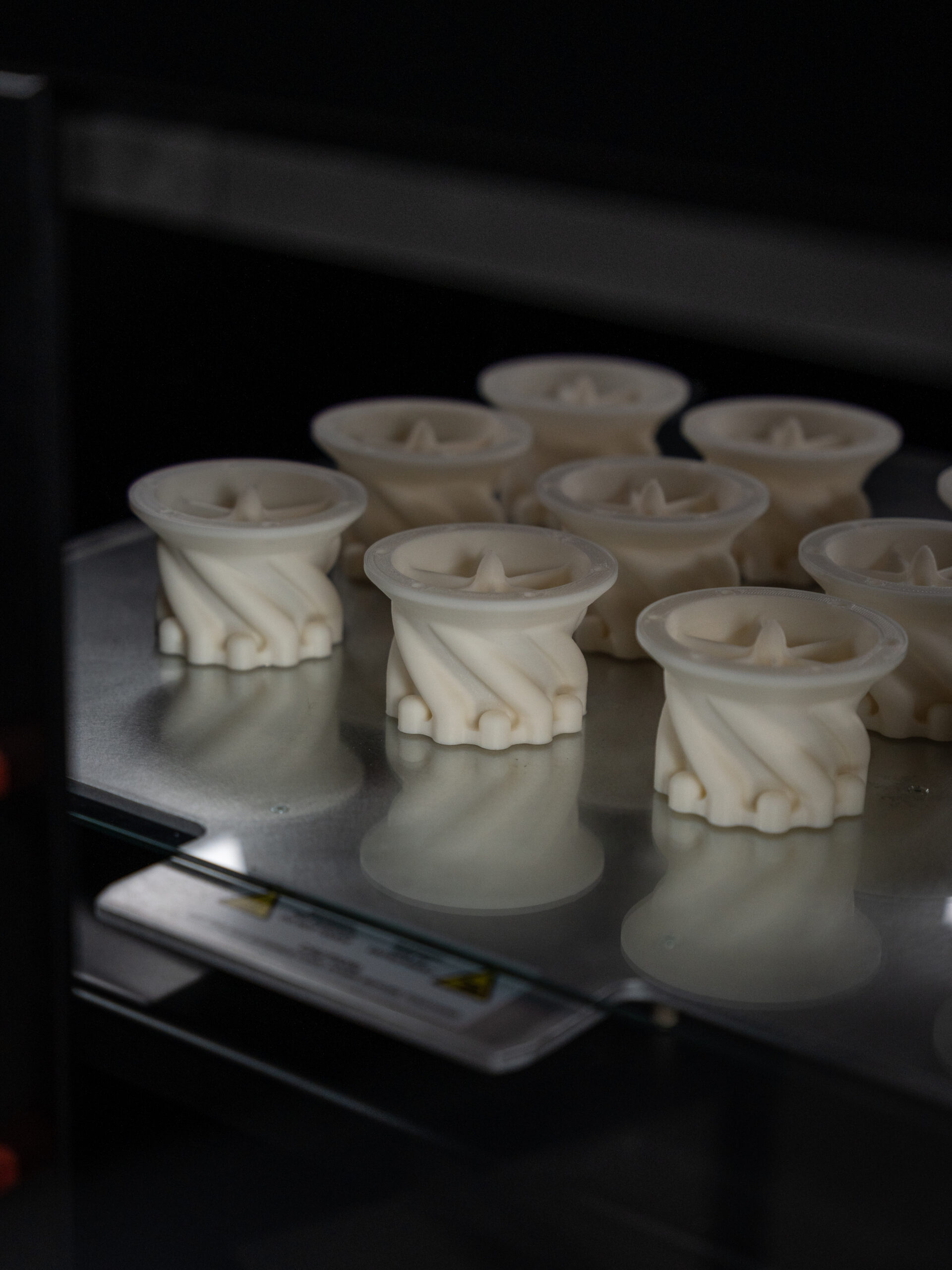
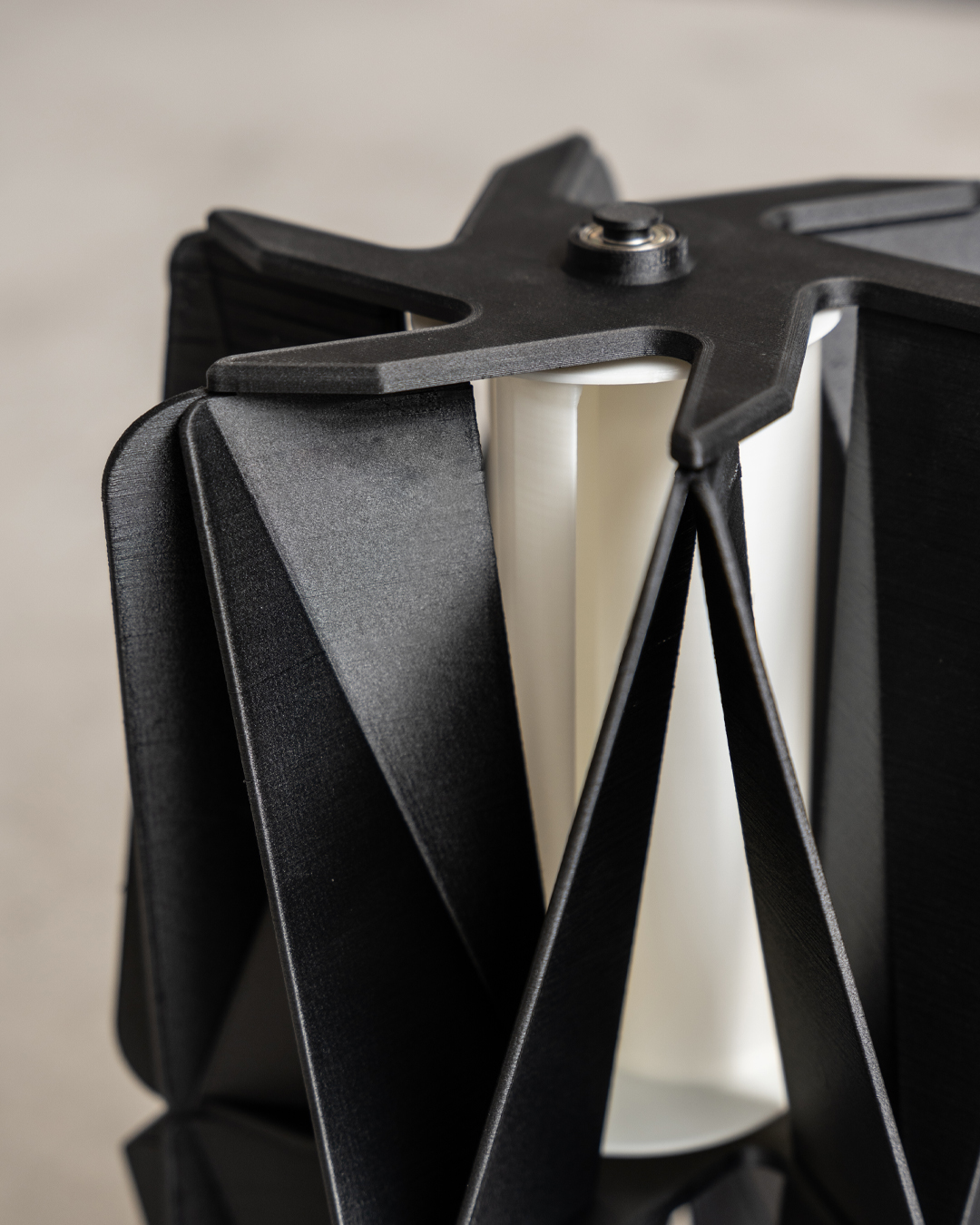
Ultimately, everything revolves around the application of your printed object. What you will print determines which filament is best to choose. Each material has its own strengths and weaknesses, suitable for different purposes. Below, we briefly discuss three popular filaments.
PLA (Polylactic Acid)

ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene)
ABS is more flexible than PLA and is less likely to break when dropped. It is therefore ideal for functional parts and industrial applications. For example, ABS is widely used in the automotive industry for parts such as dashboards and bumpers. One drawback is that ABS emits an unpleasant odour during printing. For use in office environments or at home, we recommend using a well-ventilated room, or choosing odourless filaments such as PLA or PETG.

PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG is both strong and flexible and can be stretched up to twice its own length without breaking. This unique combination makes it suitable for parts that move repeatedly or are under pressure. PETG is also approved for applications in the food industry, making it perfect for packaging, for example. Moreover, PETG can withstand high pressure without deforming, making it an ideal choice for various functional applications.