Who is Radboudumc?
Radboudumc is an academic medical center that is focused on people and their quality of life. Radboudumc specializes in patient care, scientific research, teaching and training. Their mission is to have a significant impact on health care and aim to be pioneers in shaping the healthcare of the future using personal approach and innovation. 3D printing fits very well with these ideals and is generally emerging in medicine. Radboudumc uses 3D printing for diagnostics, planning, treatment and evaluation in many different fields, such as breast reconstruction, implantology and oncology.

3D Printing in medicine
3D printing technology is on the rise in the medical sector. More and more hospitals are acquiring 3D printers for implementation in their everyday medical practice. Imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are being used to create models based on the patient’s anatomy and aid in personalized treatment. 3D printing allows far greater possibilities due to the versatility in materials, construction of complex shapes and visualization of theoretical ideas. Radboudumc utilizes 3D printing to create personalized treatment on a daily basis.
Individualized treatment
One of the 3D printing applications at Radboudumc is the electron beam radiotherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer [1]. A dddrop Leader Twin Machine is used to efficiently create a person-specific tissue equivalent material build-up, called a bolus: A CT scan is made and with it, a bolus is designed that ensures proper coverage of the tumor. A shell is created around the bolus and is 3D printed and filled up with silicone rubber afterwards. At last, the shell is removed and the bolus is ready for use during irradiation treatment.
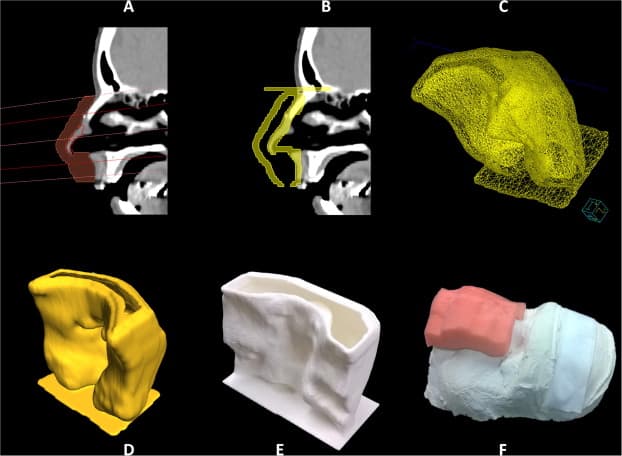
Materials
Radboudumc uses PLA for the printing of the shells. PLA is the preferred material, because of its low glass transition temperature, which makes it easy to remove the silicone rubber bolus from the shell. Printing with PLA has the advantage of almost no shrinking upon cooling, which ensures that geometrical integrity is maintained during printing. In addition, PLA is low cost and biodegradable which adds to the other advantages listed above.
Radboudumc and dddrop
Ever since purchasing the dddrop Leader Twin machine in 2016, Radboudumc has kept in close contact with dddrop. They continuously use the dddrop service plan to achieve optimal printing results and get their 3D printing questions answered. dddrop is very pleased to contribute to healthcare in this way and happy to provide the support team with an opportunity to dive into medical applications that improve the lives of many individuals.
Learn more about various 3D printing applications at Radboudumc at https://www.radboudumc.nl/en/research/radboud-technology-centers/3d-lab.
[1] Canters, R. A., Lips, I. M., Wendling, M., Kusters, M., van Zeeland, M., Gerritsen, R. M., … Verhoef, C. G. (2016). Clinical implementation of 3D printing in the construction of patient specific bolus for electron beam radiotherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 121(1), 148–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.07.011
