A new way of producing
There is no doubt that the 3D printer, with its endless possibilities, is increasingly changing the way we produce. The technology of 3D printing is in full development and partly because of this development, 3D printing is becoming more accessible and traditional production lines are becoming more efficient and fair. Remote printing certainly contributes to this. What do we mean by remote printing and what are the advantages?
Remote 3D printing
The addition of remote printing allows companies to remotely control a 3D printer from anywhere in the world. A good working network or WIFI connection gives you the ability to turn on a 3D printer in China while you are in the Netherlands or anywhere in the world. This addition brings a number of important benefits.Printing without sharing files
- Less transportation costs
- Environmentally friendly
- Time savings
Printing without sharing files
The fact that an engineer does not want to share his self-developed 3D models is not strange. The monitoring of the files and the knowledge of the engineers is very important in the product development process. Especially in the prototyping process, the files are essential to come up with a new product and this data should not fall into the hands of others. When you print remotely, you can log on to a 3D printer and order your print from anywhere in the world without sharing the data with others.
Less transport costs
Remote printing significantly reduces the need to transport goods. After all, there is no need to send physical goods around the world. All you need to send is the print order via an internet connection. The final, physical, product is then printed on site. Especially when products are produced on the other side of the world, remote printing can be a great advantage in terms of transportation costs.
Environmentally friendly
By removing transportation from the production process, a lot of fuel is saved. In the traditional production process, a product is often transported several times. After development, the product is often made by a manufacturing company in another country, then in some cases it is transported to a local packaging company and then it goes to the stores or to the manufacturer. Since the product is transported several times, many exhaust gases are emitted. Using remote printing, it is possible to produce the entire product locally, including the packaging.
Time savings
In addition to the savings in transportation costs and the environmental benefits, there is also a benefit in time savings. Global shipping takes a lot of time, even though we are spoiled with global delivery times of three days. Remote printing is much faster. The print order is given, the printer goes to work on site and a few hours later you actually have your product in your hands.
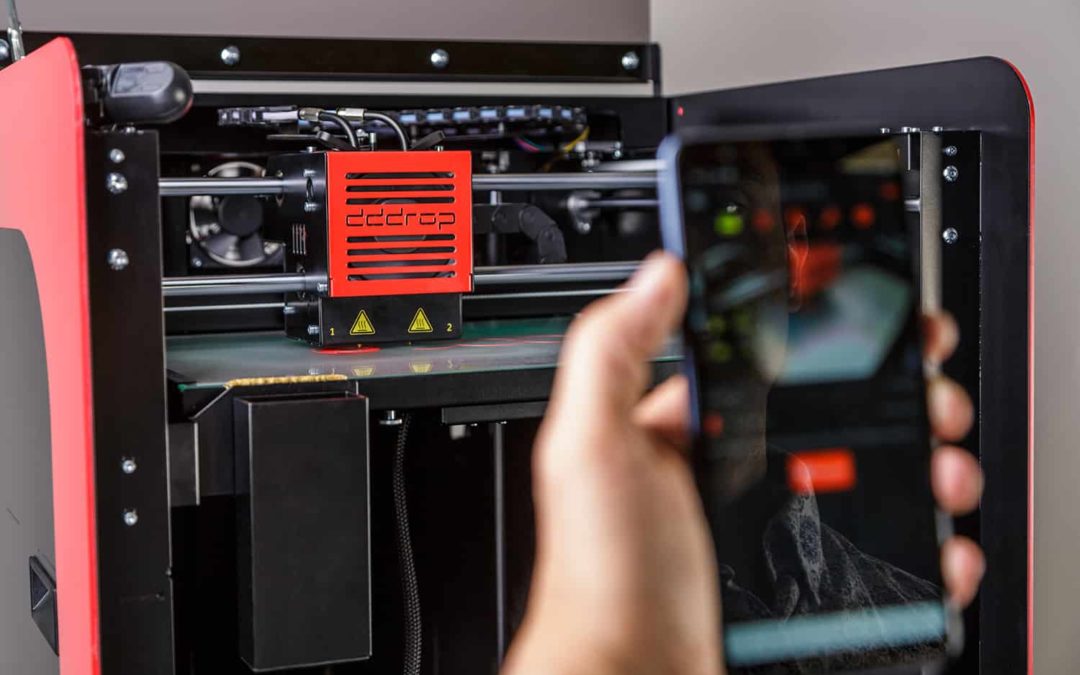
The dddrop RAPID ONE has a SMART-module which enables printing through WiFi, a Lan or a network connection. Through the useful app -that can be installed on your smartphone- and the camera in the printer, you can monitor and operate the printer at all times.